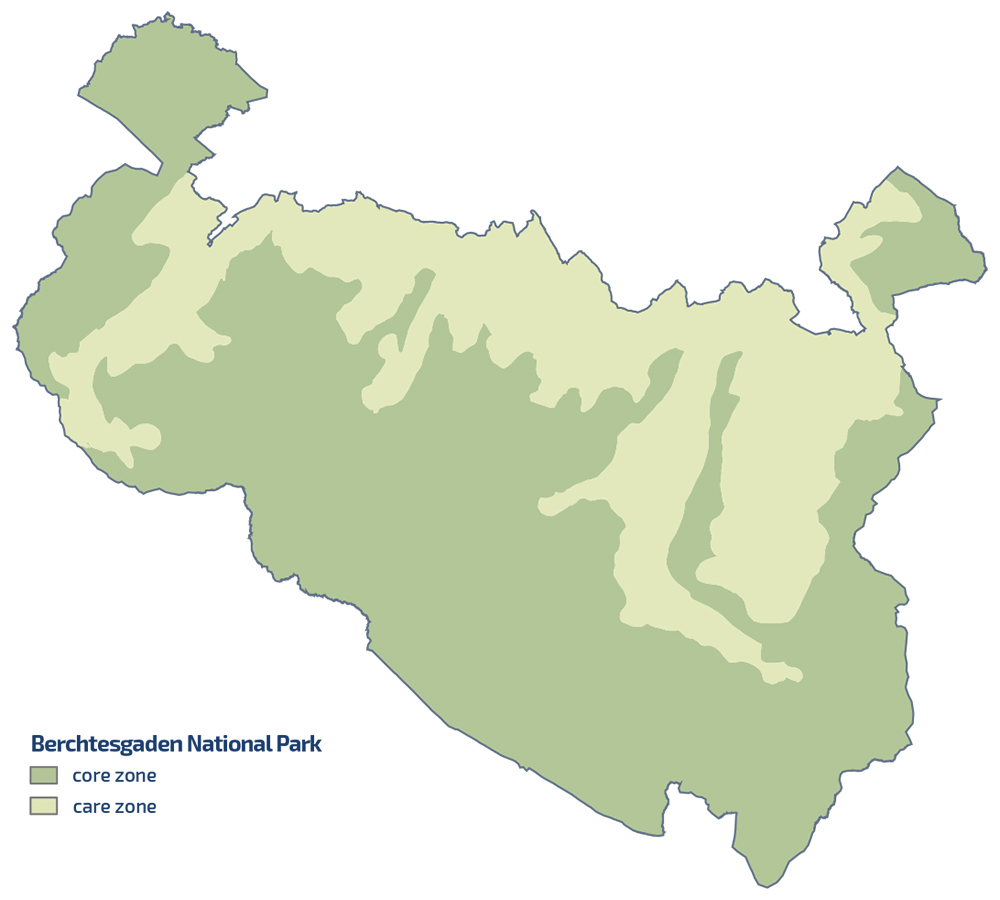
Zoning
A challenging task of the national park is to reconcile the different demands with the protection of nature. This ambitious goal cannot usually be implemented at the same time and not always in the same areas. The national park was therefore spatially divided into two zones: the core zone and the buffer zone.
Core zone: 75% of the total area
The largest part of the national park - namely three quarters, i.e. 75% - takes up the core zone. It is the heart of the national park. Here the protection of nature in its natural processes has priority, according to the motto: »Let nature be nature«. The only "uses" here are the experience of nature and the maintenance of the necessary infrastructure - all of course in line with the protection goal.
Maintenance zone: 25% of the total area
Traditional uses take place in the maintenance zone of the national park, for example shipping and fishing on Königssee or alpine farming. Alms as a valuable cultural landscape with great biodiversity can only be preserved if they are managed sustainably - as in the Berchtesgaden National Park.
In the buffer zone of the protected area there are also large areas of forest that have been used intensively for centuries as saline forests. In addition, excessive numbers of game from the days of court hunting made natural regeneration more difficult. The historical use of these forests as a fuel source for salt boiling did not follow sustainable principles at the time. The task of the national park today is to bring these forests into a state from which they can develop into healthy mixed mountain forests again.
In the buffer zone, the national park borders on its surroundings. Bark beetle management takes place at this interface. Tourist use of the national park also takes place primarily in the buffer zone.